Getting Started with Panamax: Creating an Internet-Accessible App
The world of Docker has had some very exciting releases lately. From the self-hosted PaaS Flynn having their first beta release, to the 1.0-and-beyond release of Docker itself, to the new Docker web UI from CenturyLink called Panamax and based on CoreOS, Docker has become easier to use for newcomers.
Today, I'll briefly go over how to setup and use one of these tools--Panamax--and create your own application template to produce a fully internet-accessible web application that requires zero configuration.
Docker? CoreOS? Panamax?
For those that are new to the world of Docker and friends, it may be beneficial to get an overview of how Panamax fits it--
CoreOS, a minimal operating system, is designed to work hand-in-hand with Docker-- a container management system. A container is in concept very similar to a virtual machine, since it allows for isolation of processes. Though, unlike a full blown virtual machine, a Docker container is extremely lightweight and can launch in seconds.
Docker is an extremely powerful tool, but at the same time, it is not accessible to all developers due to its command line interface, necessity for knowledge of how containers behave, and requiring for the developer to know how to edit the manifests called "Dockerfiles". This is where Panamax fits it-- Panamax provides a friendly web interface for coordinating the launch of different types of containers, such as a database and web server, and focuses on easy of use.
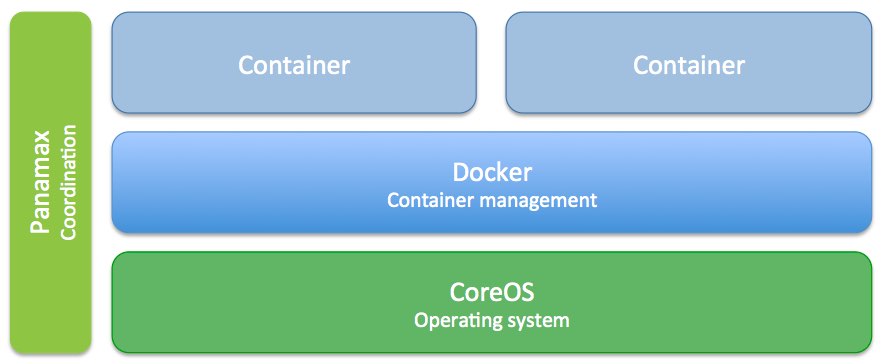
Panamax includes the ability to create application templates, or a manifest defining a set of containers to launch, as well as a repository to host this information. Historically, you've had to use the command line to use Docker with commands such as docker pull wizardapps/ngrok. After you had pulled all of the containers, you could then manually link and run them.
Now, with Panamax, this same sequence of commands is abstracted away with a single "Run Template" button. These templates are both CenturyLink and community provided, and are based on the same Docker container templates that are available in the registry. However, with Panamax, all of the linking and launching is automated with CoreOS and Fleet.
Currently, Panamax is single-host only, but CenturyLink plans on implementing multi-host support.
Installing Panamax
Due to being based on CoreOS, Panamax is currently only available as a virtual machine in Vagrant for local development. In production, you can install Panamax on various cloud providers, though it is not currently recommend due to Panamax being a new release.
No matter which platform you intend to install Panamax on, you must have two things already installed on your computer-- Vagrant and VirtualBox.
As of this article the required versions of the above software are:
- VirtualBox 4.2 or higher
- Vagrant 1.6 or higher
For an up-to-date list of required software, you can check the Panamax wiki.
Mac OS X
Mac OS X users can quickly get up and running with Panamax with a single command1:
brew install http://download.panamax.io/installer/brew/panamax.rb
After Panamax is downloaded and installed, it only takes a panamax init to bring up the CoreOS VM with Panamax preinstalled. Once the initialization command is finished, you'll see the UI pop up in your browser on port 8888.
Linux
Similar to Mac OS X, Ubuntu desktop users (12.04 and up) can run a single command:
curl http://download.panamax.io/installer/ubuntu.sh | bash
Panamax for Ubuntu will automatically open a new browser window when it is finished installing-- no need for panamax init
Basic Usage
Panamax has a couple basic commands that are important to know, though you can view all of the available commands simply by running panamax.
panamax up
The panamax up command brings the Vagrant machine running Panamax up. You can use it after rebooting your computer, for example.
panamax stop
As the name states, panamax stop will stop the Vagrant VM.
panamax restart
In reality, this is the same as a panamax stop; panamax up.
panamax reinstall
The reinstall subcommand will delete your applications and CoreOS Vagrant VM and then reinstall it. This command is useful when you need to start fresh.
You can also run panamax reinstall --memory=3072 or similar if you'd like to create a VM with more than 1 GB of memory. Personally I found the default 1 GB RAM virtual machine to be sluggish and hard to work with-- after increasing the RAM to 3 GB, the problems went away.
Launching an Application
After you have Panamax running, a good next step is to launch a pre-built application.
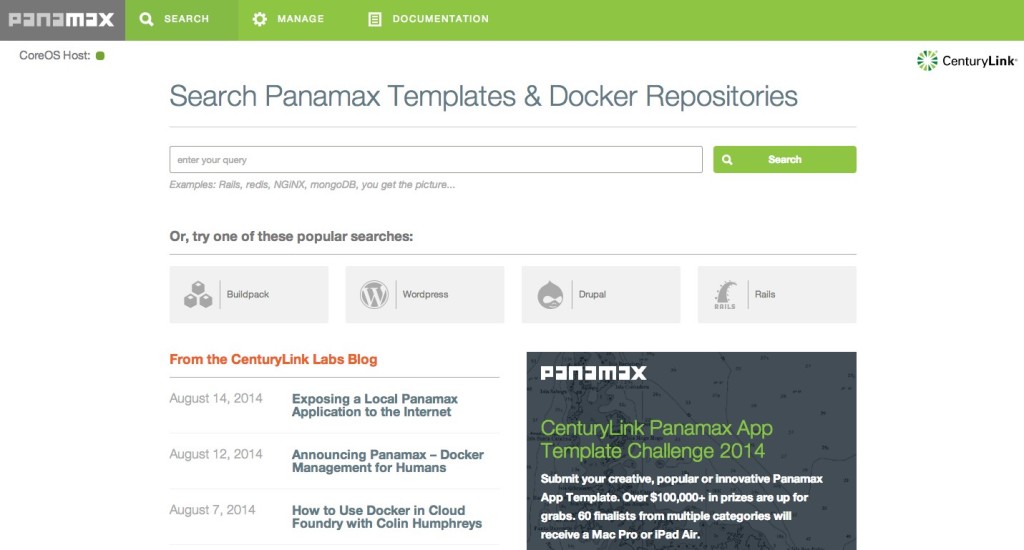
The dashboard, shown above, has several options. Most prominently you can see a search bar, which is your gateway to the Panamax template repository. The repository currently contains several applications such as Wordpress, GitLab, and others-- all pre-configured and ready to go.
Go ahead and start a search for "Ngrok + Wordpress"-- this is an application template I've created that expands on the basic Wordpress template available2.
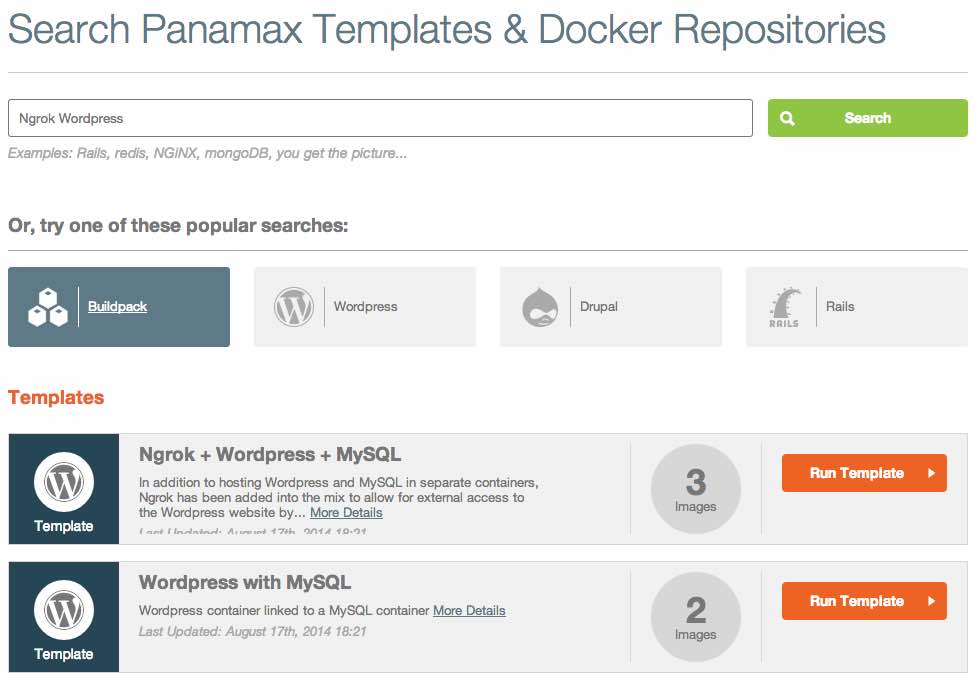
If you simply click on "Run Template" next to the "Ngrok + Wordpress + MySQL" template, you'll be brought to a new page with information on your application launch.
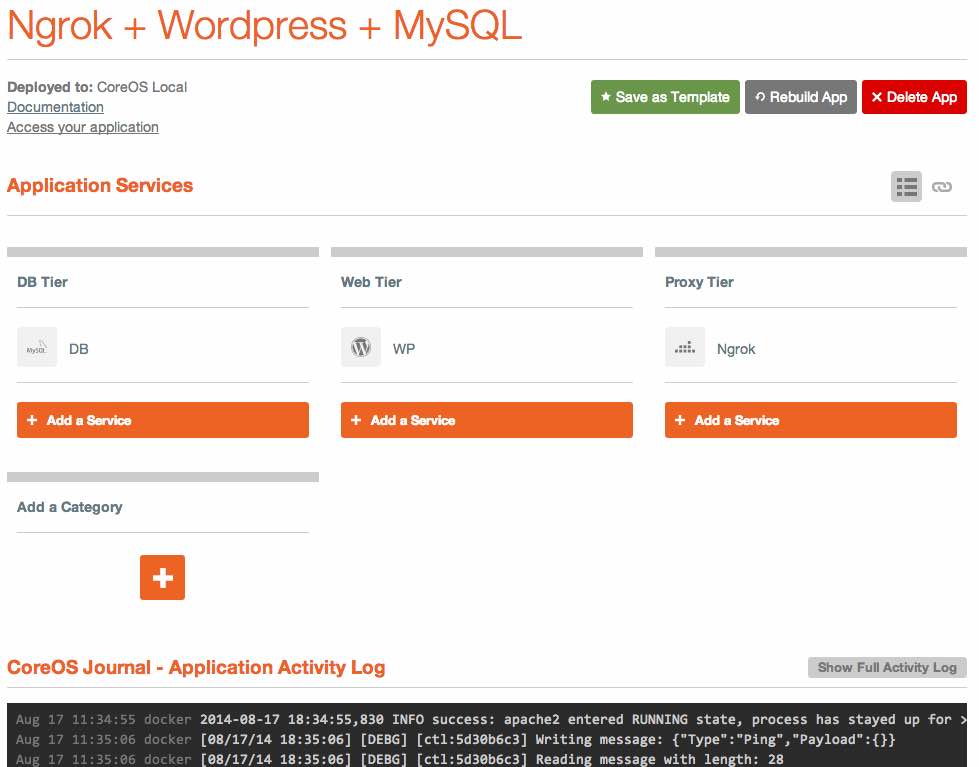
After a few seconds, you should see a message in the "CoreOS Journal" at the bottom of the page that says INFO success: apache2 entered RUNNING state, process has stayed up for > than 1 seconds (startsecs). If you see this, it means that everything is now up and running.
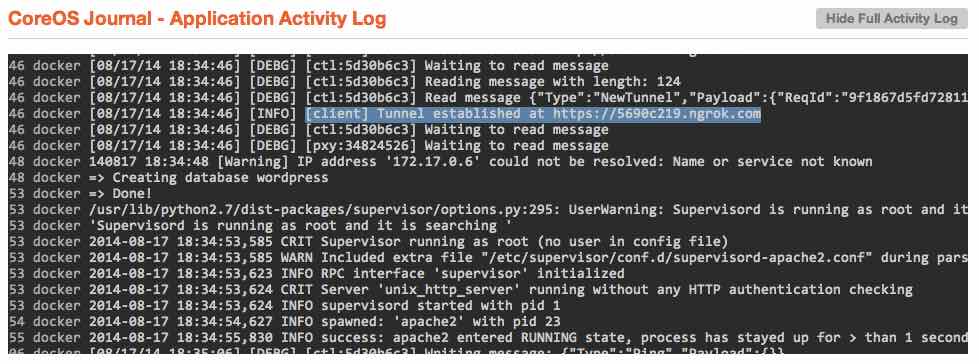
To find the publicly accessible URL, you only have to hit the "Show Full Activity Log" button above the application logs, and scroll up until you see a message that states something similar to [client] Tunnel established at https://5690c219.ngrok.com.
If you copy and paste the URL into any browser-- it doesn't have to just be on your local machine-- you'll see the Wordpress installation page pop up.
How does the Ngrok container work?
Though you may already be familiar with Wordpress, Apache, and MySQL, Ngrok may be a new concept.
Ngrok is essentially a service that creates a local tunnel from your machine, or in this case your Panamax VM inside of VirtualBox and Vagrant, are makes it accessible from the outside internet over a random subdomain. Ngrok is quite useful in scenarios where you must show a co-worker or client something that is running on your local machine, but it also makes it possible to create a publicly accessible URL through a strict firewall (or a virtual machine) without any port forwarding.
You may be asking, why would you use this complicated tunnel over simply running an app directly in Panamax? As it stands, since you must use VirtualBox to try out Panamax locally, you must perform some no-so-complicated-but-tedious steps to actually see your application in a local browser. Sure, you could follow the port forwarding instructions provided, but why do this when you can have a zero-configuration internet-accessible address you can visit from any of your devices?
In context of Panamax and your newly running Wordpress installation, Ngrok is actually running in a separate container and automatically configured through Docker links.
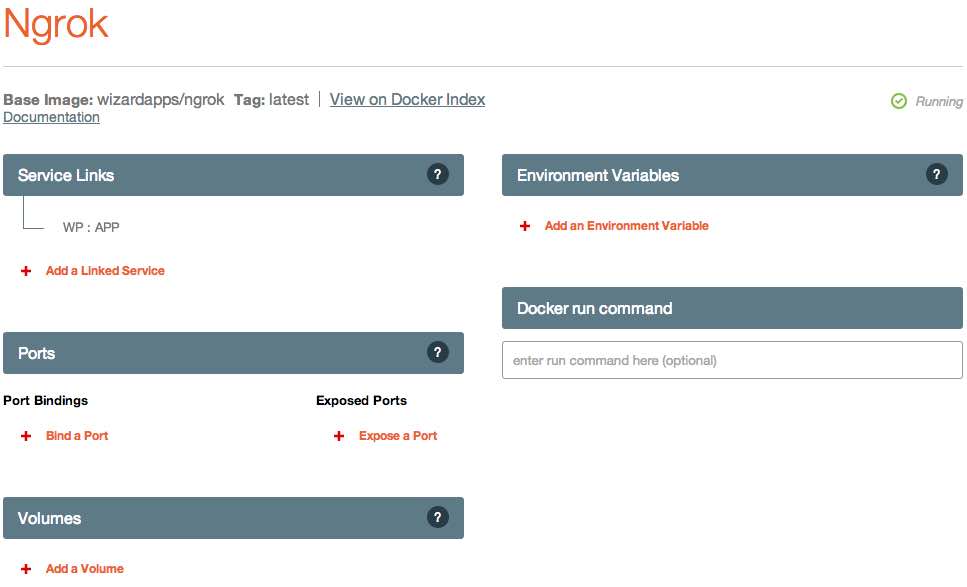
If you look at your application's page in Panamax, you'll see three tiers-- a "DB Tier", "Web Tier", and "Proxy Tier". Each "Tier" is simply a logically grouped set of containers. I've chosen to separate out each type of container based on its purpose, but this was completely arbitrary. If you create your own application template, you could put everything under a "Foobar Tier" if you wish-- there is no functional difference.
Clicking on the "Ngrok" container filed under the "Proxy Tier" category, you can see some of the inner workings of Panamax, including options for service links, ports, volumes, and environmental variables.
Ports
The ports category contains configuration on which ports are exposed or bound to the CoreOS host. This section corresponds to the Docker concept of exposing a port or binding it to a specific port on the host OS.
Volumes
The volumes section allows for you to attach volumes to the Docker container. For example, if you are creating a database container, you may wish to persist the data by mounting a volume from the host to the container.
Environmental Variables
The environmental variables section is one of the most important-- it allows you to configure your container through, you guessed it, environmental variables. For example, as I will show later on, my Ngrok container can be configured with a custom subdomain using these environmental variables.
Service Links
The final section available for configuration, and perhaps the most important for the Ngrok container, is the Service Links section. You can see a single entry containing the text "WP:APP". This single line is the magic that makes your Wordpress application accessible from outside the local VM and available to the public internet.
You may notice that other than this single link, there are no options specified to configure the Ngrok container-- no ports, IP addresses, or anything else. Like I said, by using the Docker links feature (which, is also available over the CLI3), we can make the Ngrok tunnel auto-magically configure itself.
The line "WP : APP" indicates two things:
- The Ngrok container should be linked to the "WP" container
- The "WP" container should use the alias name "APP"
The first point is not quite that exciting. However, point number two allows for the automatic configuration to "just work."
You see, the Ngrok container looks for three different environmental variables to configure itself from. In the order that the container looks for them:
- HTTPS_PORT
- HTTP_PORT
- APP_PORT
But, we never actually configure any of these environmental variables, so how can it be that Ngrok auto-configures itself? The secret is that Docker creates these variables automatically due to us linking the containers together.
If you read the Docker documentation on the links feature, you can see that several different environmental variables are created based on the link alias name:
APP_NAMEAPP_PORTAPP_PORT_[PORT]_TCPAPP_PORT_[PORT]_TCP_PROTOAPP_PORT_[PORT]_TCP_PORTAPP_PORT_[PORT]_TCP_ADDR
This is where the "APP" alias comes into play-- had the Ngrok container linked with Wordpress under a different alias (say, "WP"), the environmental variables would change to reflect this (WP_NAME, WP_PORT, etc.).
As for the variable contents, the APP_NAME is self-explanatory and not quite relevant for our use case. The APP_PORT variable, however, contains the important information for the Ngrok container to auto-configure. As you can see, it contains a protocol, IP address, and port of the linked container.
The APP_PORT_[PORT]_TCP variables contain specific configuration for multi-port-exposed containers. For example, RethinkDB uses several ports-- 8080 for the web UI, 28015 for client connections, and 29105 for intra-cluster connections. If we were to create a RethinkDB container and expose all of the previously listed ports, containers linked to the RethinkDB one would then have variables like RETHINKDB_PORT_8080_TCP_PORT, RETHINKDB_PORT_28015_PORT, etc.
In our case, Wordpress (rather, the Apache server that is serving Wordpress) only uses a single HTTP port, which is automatically placed into the APP_PORT variable.
In the startup script for the Ngrok container, you can see that we take the APP_PORT (or HTTP_PORT or HTTPS_PORT) variables and strip the protocol off.
if [ -n "$HTTPS_PORT" ]; then
FWD="`echo $HTTPS_PORT | sed 's|^tcp://||'`"
elif [ -n "$HTTP_PORT" ]; then
FWD="`echo $HTTP_PORT | sed 's|^tcp://||'`"
elif [ -n "$APP_PORT" ]; then
FWD="`echo $APP_PORT | sed 's|^tcp://||'`"
fi
This is then passed to the Ngrok program, which creates a tunnel to the Ngrok service and forwards traffic to the specified $FWD address.
If we were to use the alias name "HTTP" for the link, Ngrok would actually still configure itself properly.
So, given what we've learned, we now know how the Ngrok container auto-configures itself. In the application template I created I specified that three containers are to be launched-- one Wordpress, one MySQL, and one Ngrok. I also specified that the Wordpress container be linked to Ngrok under the alias "APP" so that the proper environmental variables are in place, and the MySQL container linked to the Wordpress one (for similar database-auto-configure functionality).
All of this happens as soon as you click the "Run Template" button, without you ever having to think about it. Quite cool, huh?
Now that you know how the Ngrok container links and configures itself, you can create your own Panamax application template based on this same principal.
Creating a Panamax Template
We'll go ahead and create a Panamax template to run PageKit, a simple CMS that runs on MySQL or SQLite, and make it accessible from the internet with Ngrok.
Creating the Application
To create the application, you simply have to search for a base Docker container to create the app from. On the home page, enter orchardup/mysql into the search bar.
Though you will see "No templates found", you will notice that there is an "Images" category. Yes, Panamax not only gives you one click access to their library of application templates, but you can actually pull in any Docker image from the public registry.
Go ahead and run the orchardup/mysql image with the "Run Image" button and let it launch. You'll see a little spinner next to the container name in the "Uncategorized" category, as well as a message in the application log indicating that the Docker image is being pulled down.
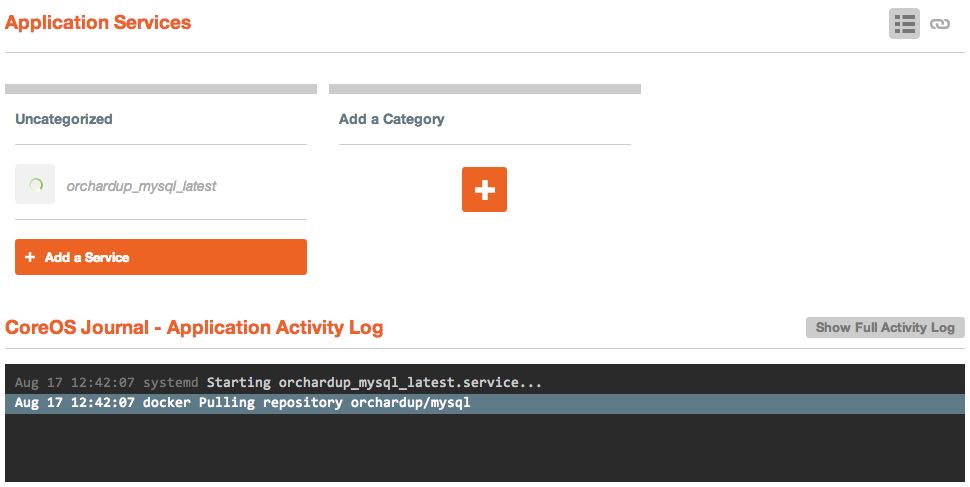
Once the image has finished pulling and launching, you should see a message indicating /usr/sbin/mysqld: ready for connections.
Though the MySQL container is running, we need to configure a couple environmental variables that will create the necessary MySQL user and database.
Under the environmental variables section, click the "Create Environmental Variable" button and enter the following variable names and values:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: Choose a password here for your MySQL root user.MYSQL_DATABASE:pagekit
If you wish to persist the database, you can always mount a volume under the "Volumes" section. To do this, enter a path on the CoreOS host to save the data in and /var/lib/mysql as the container path. This will result in all of the data in /var/lib/mysql in the MySQL container being saved to the directory you specify on the host VM.
After you've made the appropriate changes, simply hit "Save All Changes" at the bottom of the screen to relaunch the new configuration.
Notice that we didn't expose a port for MySQL-- this is because the orchardup/mysql container specifies for port 3306, the port for MySQL, to be exposed automatically. We also are not going to specify which port to map 3306 since we will make use of the Docker links.
Launching the PageKit container
Now that we have our database up and running, we can launch the PageKit container. To do so, go back to your application's dashboard4 and add a new category titled "Web Tier" if you wish. Then, add a new service and search for the Docker image marksteve/pagekit and add it to your app.
You will see that same spinning circle next to the PageKit container as it is pulled down-- you can click on the PageKit container's name and watch the activity log to determine when it has finished initializing.
Link MySQL and PageKit
Once the PageKit container has downloaded and launched, you can add a couple of configuration variables to link the MySQL and PageKit containers together, as well as expose port 80.
To create the service link, click the "Add a Linked Service" button and select the MySQL container's name from the dropdown. In the alias text box, you must use the alias name "mysql" (without quotation marks, obviously).
To expose port 80, click "Expose a Port" and enter "80" into the text box. We don't need to actually "Bind" a port because we don't need to know which host port our container's port 80 will map to-- the automatic configuration through Ngrok will just figure it out.
Once you save the configuration, the PageKit container will relaunch and link itself to MySQL. At this point, you could figure out which port was mapped to the container's port 80 and perform the VirtualBox port forwarding steps to access the application, but we'll just go ahead and launch the Ngrok tunnel.
Creating the Ngrok tunnel
Creating the Ngrok tunnel is quite easy-- as before, you can create a new category from the application's dashboard (and name is something like "Tunnel", "Proxy Tier", etc) and add a new service. We'll use the Ngrok container I've created, which was based off the CenturyLink Ngrok container5, wizardapps/ngrok.
All you have to do to configure the Ngrok tunnel is link it to the PageKit container with the alias "APP". Once the container relaunches, find the Ngrok URL in the logs and open it in your browser.
Once you open up PageKit in your web browser, you should see the installation interface. Use the following details to configure your PageKit installation:
- Driver:
MySql - Hostname:
mysql - User:
root - Password: The password you configured in the MySQL container
- Database Name:
pagekit - Table Prefix:
pk_
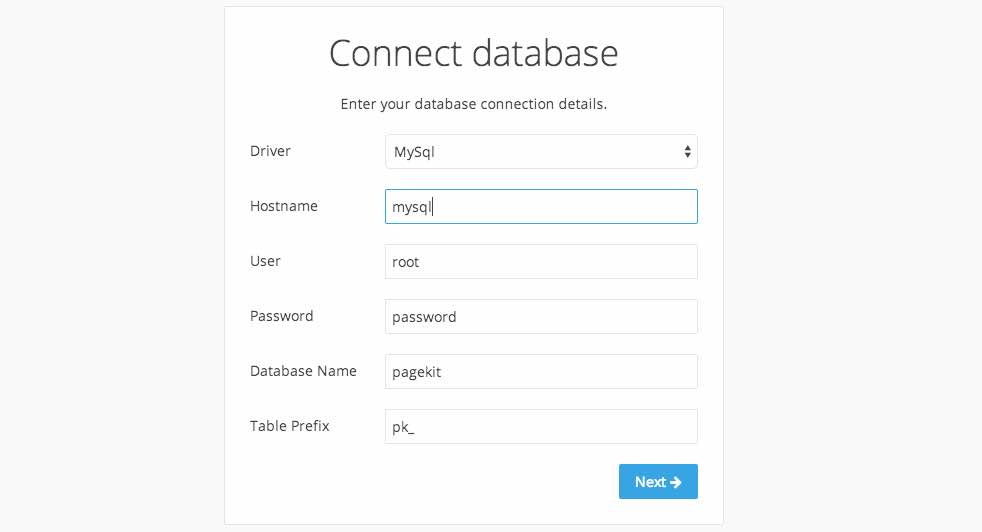
PageKit should connect to the database with these credentials. Simply finish the PageKit installation, and you're finished!
Saving the Template
Once you've created the application and played with it a bit, you can save it as an application template. Also, make sure you have a Github account (since this is where you will save the application template to).
From your application dashboard, click the "Save as Template" button. If you've never created a Panamax template before, you will need to create a Github access token and paste it into the field provided.
After you've linked your Github account, you will need to choose a repository to save the application template to. For example, you can fork the official Panamax public templates repository on Github and select your personal fork from the dropdown menu. Alternatively, you can create a new repository, though your templates will not be visible by others if you do so (unless they add your repository to their sources list).
Once you've filled out the remaining fields, you can preview the template file YAML at the bottom to see how the file is constructed, or publish your template directly to Github.
I've published the completed "Ngrok + PageKit" template on my Github repository for your reference. The only difference between the version I've published and the tutorial here is that I've manually edited some of the names of the containers for clarity.
Hopefully you've learned a thing or two about Panamax and Docker. CenturyLink has produced a fairly intuitive UI that makes Docker accessible to more people, and I'm exciting for several new features such as multi-host support. The tools popping up around Docker are exciting for the entire community, and I'm proud to be a part of it.
Ngrok Container Additional Configuration
The Ngrok container can be configured through environmental variables to support other features such as custom subdomains (or domains, if you are a paying Ngrok customer), HTTP authentication, and raw TCP protocol support.
For reference on these configuration items, you can visit the "wizardapps/ngrok" page on the Docker registry.
To use these configuration items with the PageKit template above, simply add the appropriate environmental variables to the Ngrok container. Once it is relaunched, you should be able to use the new features that you configured.
- If you don't have Homebrew for Mac, you can install it with by following the instructions on the Homebrew wiki ↩
-
Don't see the "Ngrok + Wordpress + MySQL" template? You may have to add the proper repository to Panamax. Click "Manage" at the top in the menu bar, click "Manage Sources" in the middle column, and add my Github repository:
https://github.com/andrewmunsell/panamax-contest-templates. ↩ - An important thing to notice is that all of the options on this page are simply user-friendly and web-exposed versions of the command line switches available to the Docker CLI. As I'm sure you've realized, Panamax doesn't necessarily extend Docker-- it just makes it significantly easier to manage. Also important to note-- none of the configuration categories on the page are specific to the Ngrok container. All of these same categories will be available to any container you launch. ↩
- The application dashboard is not the one with the sections such as "Environmental Variables", etc. The app dashboard has a list of all the running containers in your application, and will list the "orchardup_mysql_latest" container under "Uncategorized". ↩
- I've exposed some additional options, such custom subdomains and HTTP authentication over what was originally included in the CenturyLink Docker image ↩